Automate Your Accounts Payable: The Complete Guide to AI-Powered AP Automation

Accounts payable (AP) has long been viewed as a back‐office cost center—mired in paper invoices, manual data entry, and heavy reliance on human intervention. But in 2025, the landscape has shifted dramatically. Organizations are under increasing pressure to accelerate financial close cycles, improve cash flow visibility, and strengthen internal controls. At the same time, advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and intelligent document processing are unlocking new possibilities for end‐to‐end automation of the invoice‐to‐payment lifecycle.
Rather than treating AP as a series of isolated tasks—receive, code, match, approve, and pay—leading finance teams now embrace AP as a strategic enabler. By deploying AI‐powered AP automation platforms, they transform repetitive, error‐prone processes into agile, insight‐driven workflows. The results are clear: dramatic time savings, near‐elimination of manual errors, enhanced compliance, and the ability to reallocate talent toward high‐value analytics and vendor relationship management.
About SimplAI’s AP Automation SolutionAgentic AP Workflows: SimplAI uses intelligent AI agents to handle every step of invoice capture, matching, approval routing, and payment scheduling—automating end‐to‐end AP.Built‐in OCR & AI Validation: Our platform’s OCR + ML layers extract data from any invoice format, auto‐validate against purchase orders, and flag anomalies for instant exception handling.Seamless ERP Integration: Pre‐built connectors for SAP, Oracle, Dynamics, NetSuite, QuickBooks and more keep all your master data in sync and enable true straight‐through processing.Touchless Processing Rates >95%: SimplAI customers routinely achieve over 95% touchless invoice handling and cut their cycle times by up to 80%.Enterprise‐Grade Security & Compliance: SOC 2 & ISO 27001 certified, with end‐to‐end encryption, granular RBAC, audit trails, and built‐in fraud detection.
👉 Ready to see it in action? Book a Demo with SimplAI
Understanding AP Automation: Core Components and Technologies
What Is Accounts Payable Automation?
Accounts payable automation leverages software to orchestrate the entire invoice‐to‐payment journey without heavy manual intervention. Traditional AP relies on paper invoices, spreadsheets, and email threads—leading to delays, lost documents, and inflated headcount. Automated AP platforms, by contrast, ingest invoices (in any format), extract and validate data, route approvals, and even schedule payments based on business rules and cash‐flow optimization algorithms.
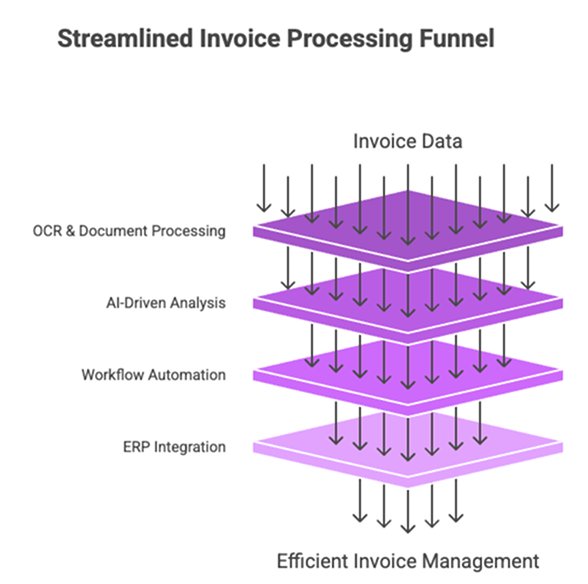
At its core, AP automation transforms unstructured invoice input into structured data. This is achieved via a series of integrated technologies that work in concert to deliver speed, accuracy, and visibility.
Key Technologies Driving AP Automation
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) & Intelligent Document Processing
Advanced OCR engines parse text from scanned documents, PDFs, and images. When combined with ML‐powered document classification, the system recognizes vendor names, invoice numbers, line‐item details, and tax amounts—regardless of layout. - Machine Learning & Artificial Intelligence
AI models learn from historical invoice data to improve accuracy over time. They detect anomalies (e.g., price variances), flag potential fraud, and recommend optimal approval paths. Predictive analytics forecast payment dates and cash‐flow impact. - Workflow Automation & Business Rules Engines
Configurable rule engines allow finance teams to define approval hierarchies by vendor, amount, department, or project. Invoices that meet criteria flow through touchless processing; exceptions are automatically routed for review, ensuring both efficiency and control. - ERP & System Integrations
Seamless bi‐directional connectors synchronize vendor master data, purchase orders, and general ledger codes with ERP systems like SAP, Oracle, or NetSuite. This integration eliminates data silos and maintains a single source of truth.
The Current State of AP Automation: 2025 Market Trends
Market Growth and Adoption Statistics
The global AP automation market is on track to surpass $6.7 billion by 2032, fueled by demand for faster close cycles and improved compliance. In 2025, over 50% of CFOs at top‐performing organizations report leveraging AI‐augmented AP solutions to detect fraud, optimize payment timing, and gain real‐time spend visibility.
Despite the compelling ROI, adoption varies. A recent industry survey found that only 14% of organizations have fully embraced AI in AP, while 41% still lack any formal automation roadmap. This gap underscores significant runway for transformation and competitive differentiation.
Artificial Intelligence Integration Trends
AI is no longer a “nice‐to‐have” but an operational imperative. Leading AP platforms now embed natural language processing (NLP) to interpret unstructured comments on invoices, automate dispute resolution, and provide conversational chatbots for vendor inquiries. Autonomous agents can even renegotiate payment terms based on cash priorities.
However, many organizations remain in pilot phases, hampered by legacy infrastructure and change‐management hurdles. Overcoming these barriers and scaling AI capabilities across finance functions represents the next wave of AP innovation.
Emerging Technologies and Future Capabilities
- Touchless Payments: AI agents autonomously trigger payments when conditions, such as early‐payment discount windows, are met.
- Fraud Prevention: Continuous ML monitoring spotlights suspicious vendor behavior or invoice patterns in real time.
- Cognitive Vendor Portals: Suppliers submit invoices via AI‐driven portals that validate data at entry, reducing downstream exceptions.
These capabilities promise to push AP toward zero‐touch processing, where exceptions are the rare exception rather than the norm.
Comprehensive Benefits of AP Automation
Operational Efficiency and Time Savings
Early adopters report an 80% reduction in invoice processing time, cutting cycle times from days to minutes. By automating data extraction and approval routing, AP teams reclaim hundreds of hours per month—hours that can be redirected toward strategic activities like spend analysis or vendor negotiations.
- Touchless Invoice Handling: With ML‐trained models, routine invoices require no human review, driving touchless rates above 95%.
- Automated Matching: Line‐item reconciliation against POs and receipts happens instantly, eliminating manual lookups.
Enhanced Accuracy and Error Reduction
Manual AP is error‐prone: misplaced decimals, duplicate payments, and coding mistakes are all too common. Automation enforces validation rules—verifying math, detecting duplicate invoices, and cross‐checking vendor master files. When discrepancies arise, the system flags them before they hit accounting records.
- Duplicate Detection: AI models learn vendor invoice patterns to identify duplicates, preventing costly overpayments.
- Coding Accuracy: Configurable business rules ensure every invoice is coded correctly, safeguarding financial integrity.
Improved Compliance and Control
Automated AP platforms create an immutable audit trail, capturing every user action and system decision. This level of transparency underpins compliance with frameworks such as Sarbanes‐Oxley (SOX), GDPR, and industry‐specific regulations.
- Segregation of Duties: Role‐based access controls (RBAC) ensure no single user can both approve and pay an invoice.
- Audit Readiness: Detailed logs and automated reporting simplify internal and external audits, reducing risk and effort.
Calculating ROI: The Financial Impact of AP Automation
Understanding ROI Components
ROI in AP automation encompasses both tangible savings and strategic gains. While direct labor reduction is easiest to quantify, benefits such as improved cash flow and vendor satisfaction have lasting impact on working capital and supplier partnerships.
Direct Cost Savings
- Labor Cost Reduction
Automating manual tasks reduces hours spent on data entry, approval follow‐ups, and exception handling. For a mid‐sized company processing 1,000 invoices monthly, this can translate to 200+ hours saved per month, or over $80,000 in annual labor cost savings. - Error Reduction & Rework Elimination
Avoiding duplicate payments and correcting coding errors prevents rework and vendor reconciliation efforts. Many organizations report 50–70% fewer exceptions post‐automation, saving both time and dispute resolution costs. - Early Payment Discounts
Faster approvals enable companies to capture early‐payment incentives, boosting savings by 1–3% of total payable spend.
Indirect Benefits and Long-Term Value
- Optimized Cash Flow Management: Predictive analytics guide optimal payment timing, balancing working capital needs with supplier expectations.
- Enhanced Vendor Relationships: Accurate, timely payments strengthen partnerships and can lead to preferential pricing or terms.
- Strategic Focus & Employee Satisfaction: Freed from routine work, AP professionals transition to roles in analytics, process improvement, and vendor engagement—leading to higher job satisfaction and retention.
Implementation Strategies: From Planning to Execution
Assessment and Planning Phase
A successful AP automation journey begins with a thorough process audit: map current workflows, invoice volumes, exception rates, and processing times. Establish baseline metrics (e.g., average days‐to‐pay, error rates) to measure post‐implementation ROI.
Evaluate existing systems (ERP, document management) and identify integration requirements or data‐quality challenges. Secure sponsorship from finance leadership and IT to ensure cross‐functional alignment.
Vendor Selection and Solution Design
When choosing an AP automation partner, consider:
- Scalability: Can the solution handle peak invoice volumes and multiple legal entities?
- Flexibility: Does the platform support custom business rules and multi‐language invoices?
- Integration: Are there pre‐built connectors to your ERP and banking platforms?
- Support & Services: What implementation, training, and ongoing support resources are available?
Design workflows to mirror—or improve upon—existing approval hierarchies. Use the opportunity to streamline bottlenecks, consolidate approval levels, and define clear exception paths.
Change Management and Training
AP automation succeeds or fails on adoption. Develop a change‐management plan that:
- Communicates Benefits: Share projected time savings, error reduction, and career‐path enhancements for AP staff.
- Addresses Concerns: Acknowledge fears around job displacement and reframe automation as a tool for higher‐value work.
- Delivers Hands-On Training: Provide role-specific training—both on system use and on new responsibilities, such as exception management and analytics.
Phased Implementation and Testing
Rather than a “big bang” rollout, adopt a phased approach:
- Pilot Phase: Start with high‐volume, low‐complexity suppliers to validate OCR accuracy and workflow logic.
- Expansion Phase: Gradually onboard additional vendors, invoice types, and business units—refining rules and exception handling.
- Full-Scale Deployment: Achieve company-wide adoption, leveraging lessons learned to optimize performance.
Include comprehensive testing—cover normal transactions, exceptions, system performance under load, and ERP integration points.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Cybersecurity Challenges in AP Automation
With greater automation comes increased exposure. AP platforms process sensitive vendor bank details and authorize payments, making them prime targets for cyberattacks such as phishing, business email compromise (BEC), and ransomware.
Implementing Security Best Practices
Protect your automated AP environment by:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for all users to prevent unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit using industry-standard protocols.
- Granular Access Controls: Enforce least-privilege principles via RBAC to limit system permissions.
- Continuous Monitoring: Deploy real-time threat detection and anomaly profiling to spot suspicious activities.
- Regular Penetration Testing: Validate platform defenses and remediate vulnerabilities proactively.
Compliance Framework and Audit Requirements
AP automation must support SOX, GDPR, and tax reporting regulations. Ensure the system:
- Maintains a complete, immutable audit trail of all invoice and payment actions.
- Enforces segregation of duties, preventing conflicts of interest.
- Provides out-of-the-box compliance reports for internal and external auditors.
Collaborate with legal and audit teams early to map platform capabilities to regulatory requirements.
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
Advanced AI and Machine Learning Applications
The next frontier in AP automation centers on cognitive exception resolution—AI agents that autonomously handle common disputes and escalate only truly novel cases. Expect to see:
- Natural Language Invoice Interpretation: NLP models that understand free‐text remarks and map them to accounting codes.
- Predictive Cash Flow Forecasting: Real‐time dashboards combining AP data with accounts receivable and treasury positions.
Integration and Collaboration Trends
AP will no longer sit in isolation. Future systems will seamlessly connect:
- Procurement Platforms: Enabling closed-loop procure-to-pay with automated PO creation from purchase requisitions.
- Supplier Networks: Real-time invoice submission portals that validate data at entry and provide status updates.
- Treasury Management Systems: Automating payment execution based on cash availability and risk thresholds.
Real-Time Processing and Instant Payments
Instant payment rails and real-time bank APIs are maturing. Organizations will leverage dynamic discounting—where AI agents negotiate early-payment terms automatically—and real-time remittance advice, delivering immediate payment confirmation to suppliers.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Accounts Payable
AP automation represents a paradigm shift—from manual, error-prone processes to intelligent, agentic workflows that drive efficiency, compliance, and strategic value. Organizations that invest now in AI‐powered AP solutions position themselves for:
- Immediate Cost Savings: Through labor reduction, error avoidance, and discount capture.
- Enhanced Controls: With immutable audit trails, RBAC, and fraud detection.
- Strategic Focus: Freeing AP professionals for analytics, policy optimization, and vendor engagement.
The journey requires careful planning, technology selection, and change management—but the payoff is transformational. Early adopters will not only streamline finance operations but also gain a competitive edge through superior cash‐flow management and stronger supplier partnerships.
👉 See SimplAI in action with a personalized demo: https://simplai.ai/request-demo
Frequently Asked Questions About AP Automation
What is the difference between AP automation and traditional invoice processing?
Traditional processing relies on manual data entry, paper documents, and email approvals. AP automation uses OCR, AI, and workflow engines to digitize invoices, extract data, enforce business rules, route approvals electronically, and schedule payments—freeing humans to handle exceptions and strategic tasks.
How long does implementation take?
Timelines vary by complexity. A basic setup for a small‐to‐mid-sized business can take 6–12 weeks, while enterprise deployments with complex workflows typically run 6–12 months. Phased rollouts—starting with high-volume, straightforward invoices—are recommended.
What ROI can I expect, and when?
Most organizations see measurable gains within the first 3–6 months, achieving up to 80% ROI in year one. Savings accrue from reduced labor, error avoidance, early-payment discounts, and improved cash management.
Will automation eliminate finance jobs?
No—automation shifts roles from routine data entry to exception management, analysis, and vendor relationship management. Proper change management and retraining ensure that AP professionals upskill and remain highly engaged.
How does integration with ERPs work?
Most platforms offer pre-built API connectors or direct database integrations for major ERPs (SAP, Oracle, Dynamics, NetSuite, QuickBooks). These integrations sync vendor master data, purchase orders, and GL codes, and push processed invoices back for payment.

